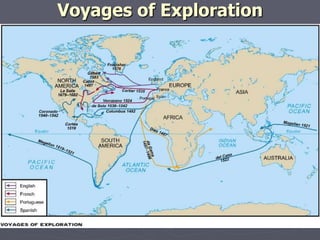
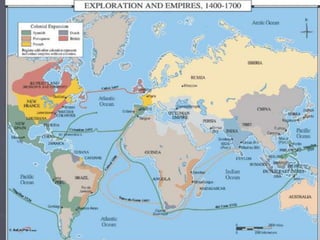
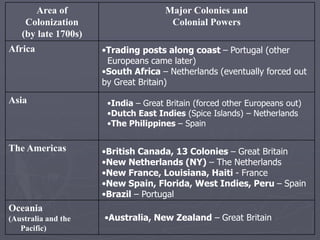
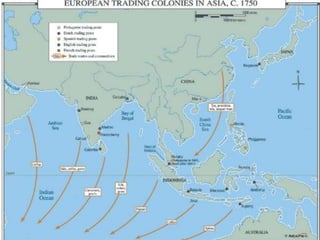
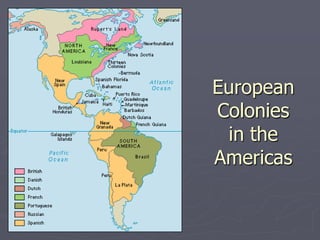
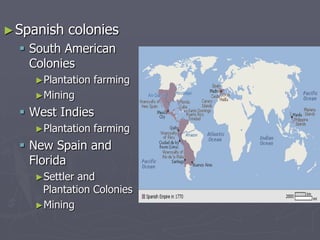
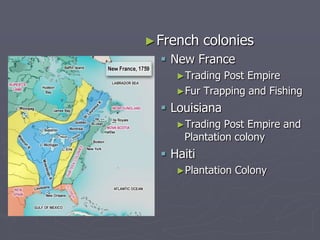
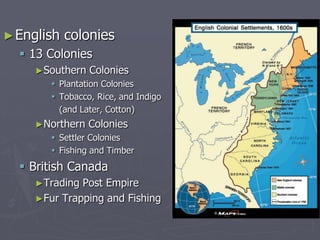
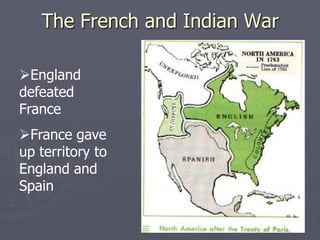
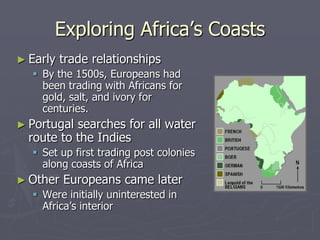
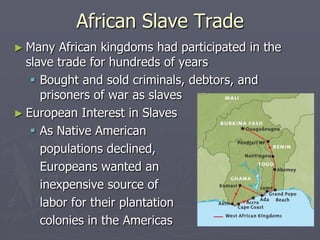
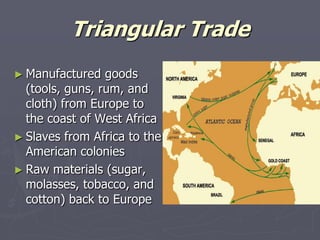
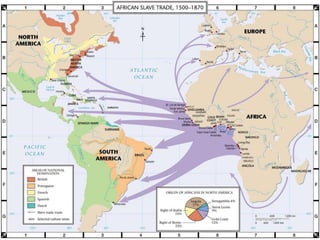
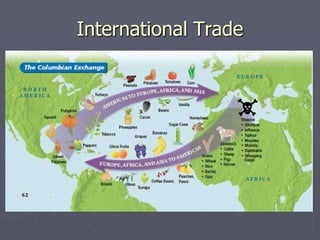
Europeans explored and colonized much of the world between the 1400s and 1700s for reasons such as trade, religion, and glory. They established trading posts and settlements in Asia, Africa, and the Americas. This led to immense political, social, and economic changes, including the rise of new empires and the spread of Christianity and European culture. It also involved exploitation such as the Atlantic slave trade and the transfer of wealth from colonies to European powers. By the late 1700s, capitalism had begun to replace the system of mercantilism in guiding international trade.